Great article with header description:
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/docs/DOC-26145
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet_frame
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.1Q
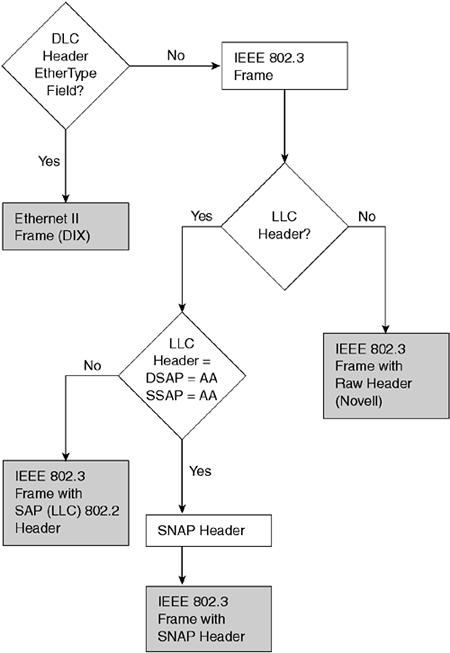
The SNAP is an extension of the 802.2 LLC specified in the IEEE 802 Overview and Architecture document.[2] The 5-octet SNAP header follows the 802.2 LLC header if the destination SAP (DSAP) and the source SAP (SSAP) contain hexadecimal values of AA or AB:
| 802.2 LLC Header | SNAP extension | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSAP | SSAP | Control | OUI | Protocol ID |
| 1 octet | 1 octet | 1 or 2 octets | 3 octets | 2 octets |
The SNAP header consists of a 3-octet IEEE Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) followed by a 2-octet protocol ID. If the OUI is hexadecimal 000000, the protocol ID is the Ethernet type (EtherType) field value for the protocol running on top of SNAP; if the OUI is an OUI for a particular organization, the protocol ID is a value assigned by that organization to the protocol running on top of SNAP.
SNAP is usually used with Unnumbered Information 802.2 protocol data units (PDUs), with a control field value of 3, and the LSAP values are usually hexadecimal AA, so the 802.2 LLC header for a SNAP packet is usually AA AA 03; however, SNAP can be used with other PDU types as well.
On Ethernet, the 8 octets occupied by the LLC and SNAP headers reduce the size of the available payload for protocols such as the Internet Protocol to 1492 bytes, compared to the use of the Ethernet II framing; therefore, for protocols that have EtherType values, packets are usually transmitted with Ethernet II headers rather than with LLC and SNAP headers. On other network types, the LLC and SNAP headers are required in order to multiplex different protocols on the link layer, as the MAC layer doesn’t itself have an EtherType field, so there’s no alternative framing that would have a larger available payload.